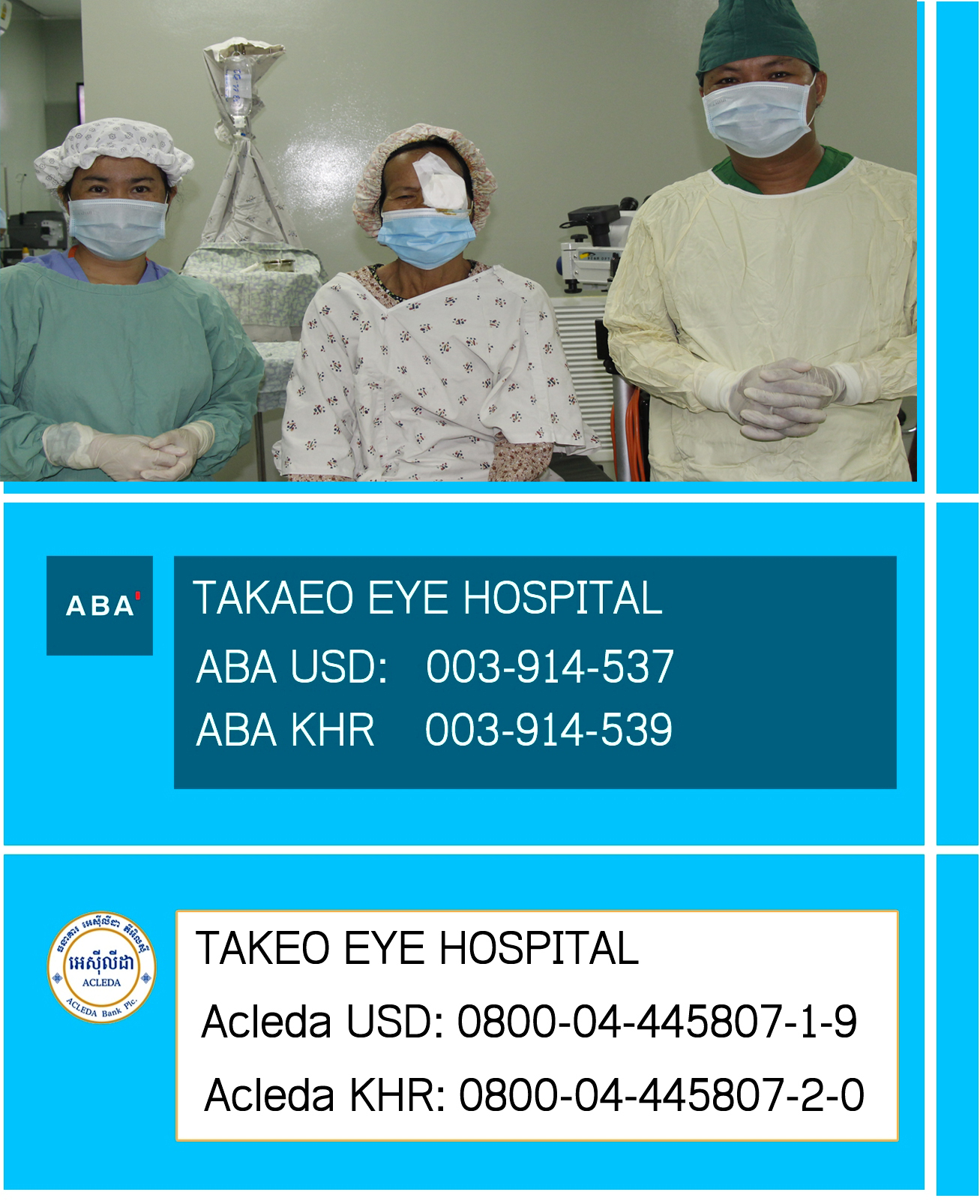
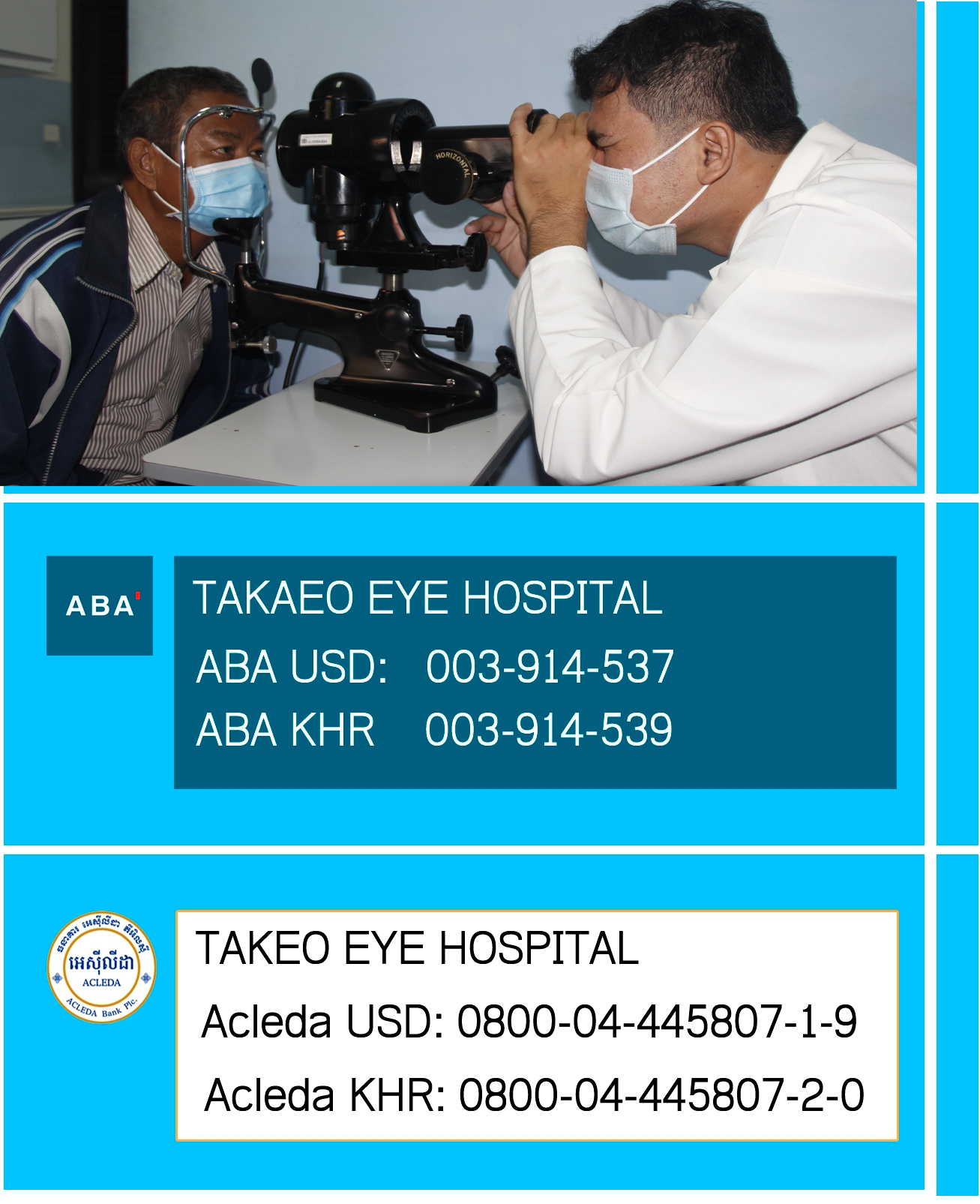
| Our Target Area Takeo Province is located in Southern Cambodia, it is about 80 Km far from Phnom Penh city. It borders Kampong Speu to the North, Kandal to the East, Vietnam to the South and Kampot to the West. The topography is variable, from the Bassac River floodplains to the east, through a broad belt of lowland paddy fields occupying much of the province, to smaller areas of lowland/ upland mosaic on parts of the Western and Southern borders. Takeo Province is classified as a rural province and has 10 districts, 100 communes with 1,111 villages. Takeo Province has 980,232 population and 3,563 square kilometres big with the population density of Cambodia in 2011 was therefore 259.5 people per square kilometer against national 75; it is the highest figure if compare to other provinces in Cambodia because there have a rapidly growth 0.66 % rates over years in small geography area. The quantity of children census 2008 illustrated that Takeo province has high figure 297,622 (boy: 153, 676, girl: 141, 946) of total population. 1.5% of people with disabilities and prevalence of blindness is 2.8% in 2012. Life expectancy of Takeo was not specific calculated, but it is normally used through national calculation of general population in Cambodia is an average around 62.67 years, male: 60.31 years female: 65.13 years (2011 est.)Direct Target Groups: All people such as women, children, men, and people with disabilities in Takeo Province and surrounding provinces who have eye health problems. Indirect Target Groups: Family members and communities of people with eye health problems and medical professionals who are trained during the project.Target groups include all persons regardless of their sex, age, religion and social and economic status. We make special efforts to make our services available, affordable and accessible (physically and socially) to the economically poor, persons with disability, elderly persons, children, women and people living with HIV/AIDS and people who can afford the services. For example, the hospital’s physical design (ramps, large signs, and disabled toilets), the provision of free transport and food to CTEH (from remote villages), |